Water is one of the most essential resources in the energy sector. For Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB), responsible water management is central to ensuring business continuity, protecting the environment, and securing long-term sustainability. In 2025, TNB strengthened its commitment to water stewardship by introducing a comprehensive water reduction target to achieve a 15% reduction in water consumption intensity by 2035, with 2025 as the base year.
The Sustainability & Energy Transition Committee (SETC), chaired by the President/Chief Executive Officer, plays a pivotal role in advancing this commitment. Supported by members of TNB’s top management, the Committee ensures that water efficiency and sustainability principles are embedded in strategic decision-making across the organisation.
This governance framework goes beyond regulatory compliance, supporting consistent operations and responsible resource management. Through this integrated approach, TNB continues to strengthen its leadership as a responsible energy provider, balancing power generation demands with the sustainable management of water resources.
Understanding TNB's Water Footprint
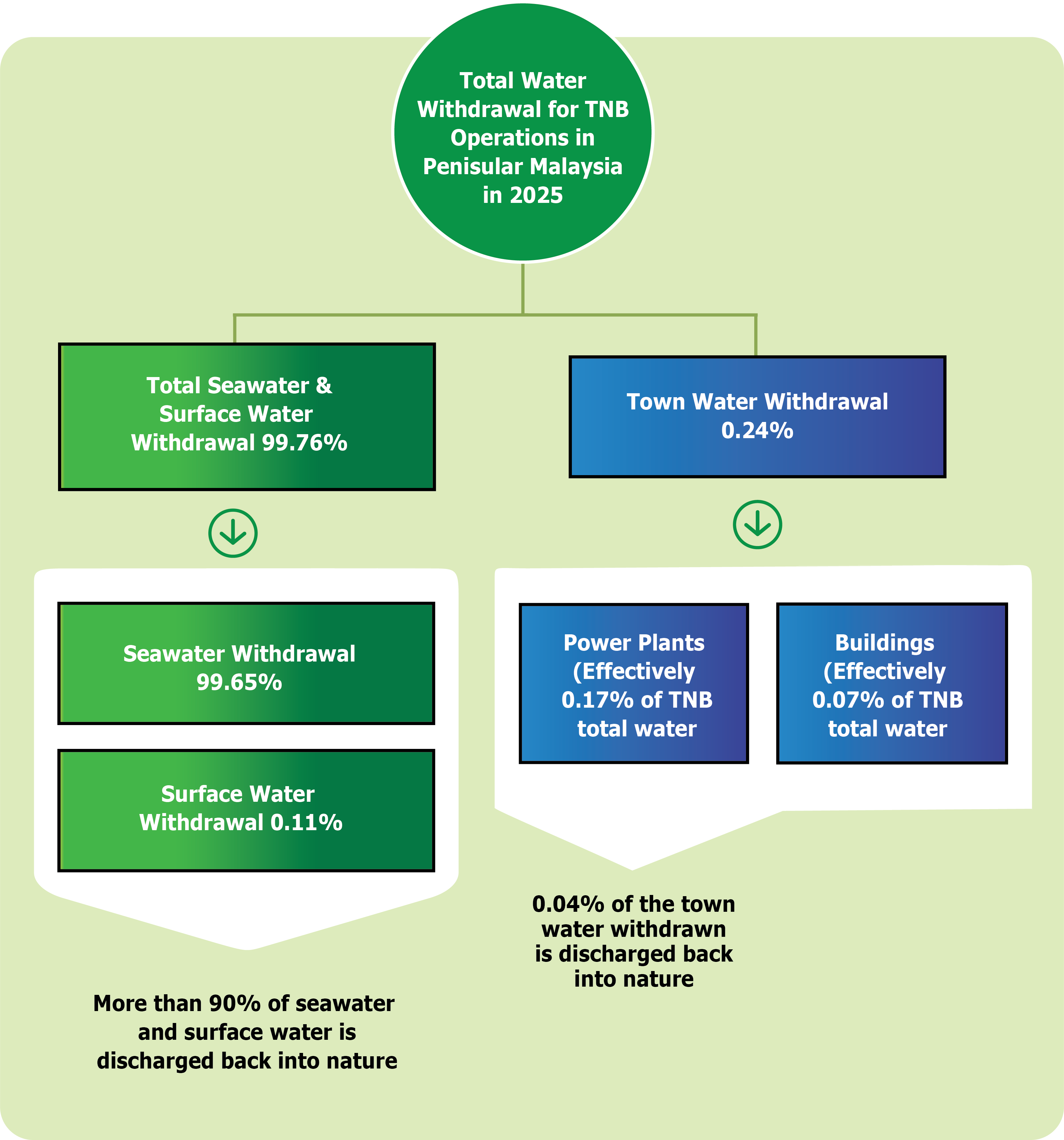
TNB’s operations involve significant interaction with water resources, particularly within power generation. Approximately 99.76% of total water withdrawal comes from seawater and surface water - used mainly for cooling with more than 90% of this volume is safely discharged back into the environment. Only 0.24% of total withdrawal represents town water consumption, which constitutes TNB’s actual water use.
Despite this low percentage, TNB recognises the opportunity to reduce consumption further through efficiency and technological innovation. Around 60% to 70% of total water consumption is utilised by TNB’s thermal power plants, while the remaining 30% to 40% is consumed across other business segments, including office buildings and substations.
To capture the most material impact, TNB’s long-term water reduction target focuses on the power generation segment, where consumption intensity improvements can deliver the largest gains in both environmental performance and operational efficiency.

Prai Power Plant

Southern Power Generation (SPG)
Translating Commitment into Measurable Progress
TNB’s continuous efforts to embed sustainability in operations have been producing tangible outcomes. Through several targeted initiatives, the company demonstrates how everyday operational changes translate into measurable water savings.
-
1. “Drip by Drip, Watt by Watt”Introduced to instill a culture of water mindfulness, this initiative covers 109 office buildings across TNB. In 2025, our water-efficiency initiatives achieved a savings of 2,181 m³, representing a 3.3% reduction against the corresponding period in the previous year, showcasing how consistent monitoring and behavioral changes at the workplace can create lasting impact.
-
2. Zero-Leakage Valves in Thermal Power PlantsTechnical upgrading has been key to improving efficiency. The installation of zero-leakage valves at power stations has led to significant water output reductions - 58% at Prai Power Plant and 73% at Southern Power Generation (SPG) facilities. These achievements exemplify how engineering-based solutions can strengthen operational reliability while conserving valuable resources.
-
3. Rainwater HarvestingTNB has implemented rainwater harvesting systems at TNB Platinum and Balai Islam, located at the headquarters in Kuala Lumpur, resulting in the collection and reuse of 8.37 megalitres in 2025. This initiative not only reduces reliance on town water but also serves as a scalable model for future infrastructure.
Together, these initiatives contribute to overall reductions in water consumption across non-generation facilities, providing a foundation for further expansion across other business units.

Rainwater harvesting tank at TNB building

Rainwater harvester at TNB building
Comparative Efficiency and Transition Outlook
On average, TNB’s gas plants have lower water consumption in terms of intensity compared to coal plants. The analysis reveals that gas-fired plants consume less water per unit of energy generated (0.058 ML/GWh) compared to coal-fired plants (0.135 ML/GWh). TNB’s ongoing transition to a cleaner generation mix, reducing coal capacity by 50% by 2035 and expanding gas and renewable energy generation, will directly lower water consumption intensity.
This structural shift forms the backbone of TNB’s water intensity reduction strategy, enabling a forecasted 15% reduction by 2035.
TNB’s water reduction initiative is guided by three (3) key factors focused on operational efficiency, energy transition, and resource circularity:
1. Operational Efficiency and Technology Adoption
Integrating smart water-use technologies, automated leak detection, and closed-loop cooling systems, alongside infrastructure upgrades during plant refurbishment and repowering projects.
2. Transition to a Cleaner Energy Mix
Phasing down coal dependency and expanding gas and renewable generation to significantly lower overall water intensity.
3. Water Circularity
Scaling up rainwater harvesting and recycling initiatives across corporate and operational facilities.
TNB’s water reduction journey also supports the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by advancing cleaner water management, responsible resource use, and climate action. Specifically, these efforts align with SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action) - demonstrating how TNB’s operational initiatives contribute to global sustainability priorities.



Looking Ahead: Every Drop Counts
Integrating efficiency, innovation, and circularity across operations, TNB is not only reducing its water consumption intensity but also reinforcing its role as a responsible energy provider. Our 15% reduction target by 2035 reflects a forward-looking approach - balancing Malaysia’s growing energy needs with the protection of vital natural resources, ensuring that every drop counts toward a more sustainable future.