Driving Sustainable Operations
At TNB, our commitment to sustainable operations includes a dedicated focus on optimizing water consumption, especially within our power generation processes. With power plants constituting about 80% of our water usage, our innovative measures are specifically designed to optimize process water consumption. All our generating power assets are built and operated in accordance with global “World Bank Environmental and Social Standards” based on the initial project bidding requirements and include water consumption process which is archetypical of conventional high efficiency thermal plants. Additional efforts are also taken at operational level to illustrate our commitment to responsible resource management, underscoring our proactive efforts in fostering sustainability within our operations.
Closed-Loop Water Usage for Steam Generation
Water consumption plays a pivotal role in our steam generation process, forming a closed-loop system aimed at minimising our reliance on municipal water sources. This system is crucial for sustainable operations as it significantly reduces our water withdrawal from municipal supplies. Essential to the efficient functioning of our boilers is the continuous introduction of feedwater, known as makeup water, into the system. Effective management of makeup water is paramount for ensuring optimal boiler performance, overall power plant efficiency, and safety. The careful control and quality assurance of makeup water is fundamental; any inadequacy or impurity in this supply may not only compromise efficiency but also pose significant safety hazards within our operations.
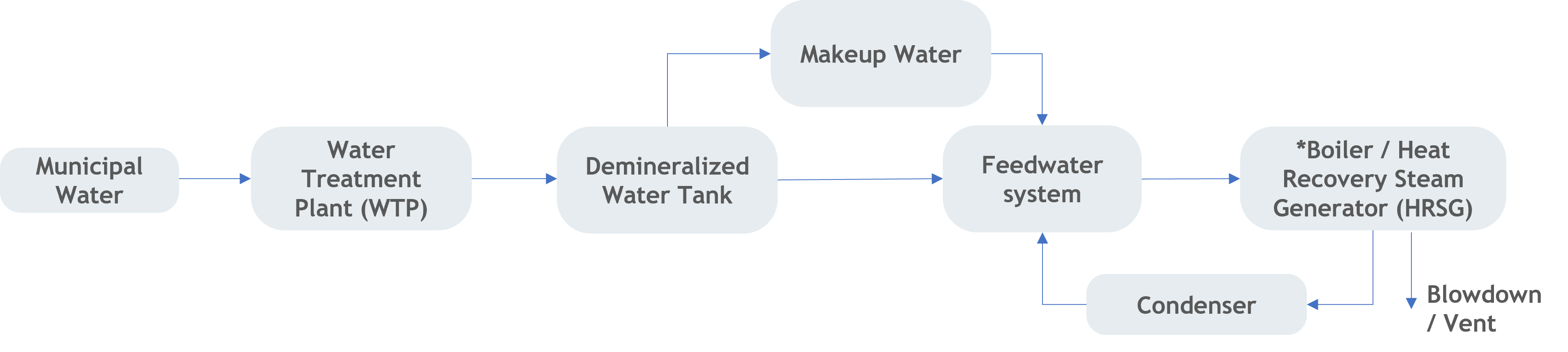
Simplified process of feedwater for steam generation
Generally, in many power plants, makeup water constitutes a relatively small fraction of the total feedwater, often hovering between 1% to 5% depending on plant operating conditions and dispatch requirements by the grid system operator. Within power plant operations, a shared objective revolves around decreasing this makeup water percentage through strategic measures such as maintaining water treatment quality, blowdown minimisation, and leak prevention. As a result, TNB’s thermal power plants utilize water for makeup purposes, with proportions ranging from 1.87% to 3.08% in relation to the feedwater (depending on the plant respective efficiencies and water cycle design). This concerted effort toward reducing makeup water serves as a cornerstone in our commitment to conserving water resources and fostering sustainability within our operations. By implementing these practices, TNB actively contributes to the efficient use of resources while advancing our sustainability initiatives.
As pioneers of Combine Cycle Gas Turbine and Ultra Super Critical Boiler technology in South-East Asia, we are dedicated in our commitment to operational excellence. Through our proactive 'Operational Excellence' best practices and 'Business Turnaround Program' initiated in 2017, we persistently monitor and execute water conservation initiatives within power plant operations. Our comprehensive methodology allows us to meticulously identify, plan, and implement impactful strategies for conserving water resources. Furthermore, we specialize in state-of-the-art reverse engineering and plant upgrade initiatives, aligning with our dedication to achieving world-class operational performance in power plants. Some tangible examples of initiatives implemented by TNB Power Generation Sdn. Bhd. includes:
- Boiler combustion tuning for our coal fired boilers and gas turbine tuning to optimize water circulation ratio and feed water consumption when consuming fuel of diverse quality.
- Continuous upgrade of high-pressure valve materials to sustain continuous operation at zero leak and passing conditions.
- Periodical inspection on condenser using both on-line and off-line method to identify and reduce condenser tube leak incidents.
- Pre-emptive thermography & thermal scanning prior to plan outages to correctly identify and replace leaking valves.
- Improving feed water heaters and economizer temperatures by reducing spray water cooling upstream of condenser neck
The total municipal water consumption at TNB power plants in 2022 is disclosed in TNB Sustainability Report 2022.
Water Sources for Power Plant Cooling Systems
Water plays a dual role in our plant operation, serving not only as a vital element in steam generation but also as a crucial component within our cooling systems. To effectively reduce our dependence on municipal water sources, we use water from alternative sources such as seawater or river water1. Our cooling process, facilitated through the open circuit Main Cooling Water (MCW) system, operates efficiently by utilising seawater or river water and subsequently discharging it back into the sea or the river at the regulated operating temperature. This ensures zero net water consumption, exemplifying our commitment to sustainable practices by minimizing environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency and adhering to global water conservation standards set forth by Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI).
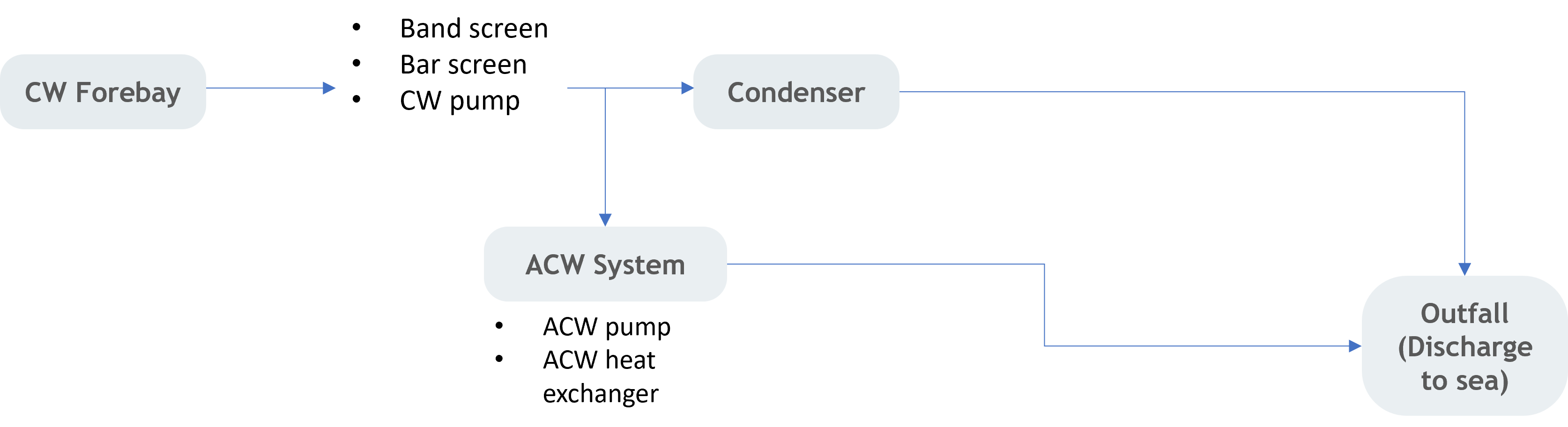
Simplified process of Main Cooling Water (MCW) system
The total seawater withdrawal volume of 3,853,723 megaliters for FY2022 for TNB's coal power plants2 can be viewed as a conservation measure for municipal water used in power plant operations.
1. TNB Connaught Bridge Sdn Bhd is the only thermal power plant that extracts water from a river source for cooling purposes.
2. Excluding KEV as data collection is still in progress.
Enhancing Water Quality Monitoring at Discharge Points
At the water discharge point of power plants, water undergoes thorough treatment to meet environmental standards and prevent harm to the ecosystem. Key parameters such as pH, temperature, oil & grease, total suspended solids, and specific contaminants like heavy metals are measured to ensure compliance.
The Waste Water Treatment Plant (WWTP) employs sedimentation, filtration, and chemical processes to eliminate pollutants. The Environmental Management System (ISO 14001) guides monitoring to ensure compliance with Environmental Quality (Industrial Effluent) Regulations 2009. While most plants adhere to Standard B limits, Sultan Ibrahim Power Plant (SPG) complies with the more stringent Standard A limit. Despite these stringent measures, power plants consistently uphold specified water quality standards at discharge points.
Way forward: Strengthening our approach to water management
We are proud to unveil our Water Management Roadmap, a pivotal step towards sustainable and responsible water usage practices. This Water Management Roadmap, approved by the Sustainability & Energy Transition Council (SETC) chaired by the CEO of TNB, charts the course for our efforts in water sustainability. We recognise the crucial role of water in our operations and the communities we serve, and our roadmap is designed to ensure responsible water usage and conservation across all facets of our business.
Water Management Roadmap – Key Milestones.
|
2023 |
2024 onwards |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
June |
July |
August |
September |
October |
November |
December |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Key milestones within this roadmap include the revision of the TNB Environmental Policy, emphasising the CEO’s and TNB management’s commitment towards the conservation of water in ensuring that our commitment to sustainable practices is embedded in every aspect of our operations. Additionally, the enhancement of the SETC Terms of Reference (TOR) aligns our organizational goals with the highest environmental standards.
As part of this forward-looking initiative, we have introduced the Water Management & Inventory System (WAMI) that has been developed for comprehensive data collection, thus allowing us to monitor and evaluate our water withdrawal and consumption practices with more precision. The official rollout of WAMI in October 2023 marks a significant stride toward transparency and accountability in our water management practices.
In line with our water conservation policy, we will leverage the comprehensive data gathered from the WAMI to establish a baseline for our water withdrawal and consumption. This analysis serves as a foundational step in understanding our current usage patterns, enabling us to craft an informed water optimization strategy. With this detailed insight, we're poised to set granular targets for optimizing water consumption across our operations. We are dedicated to reducing building water consumption by 2%.
At TNB, we recognise that water is a finite resource, and our commitment to water efficiency is not just a responsibility but also a testament to our dedication to sustainable practices and resource conservation.