A Milestone in Biodiversity Management
In 2024, Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB) launched its Biodiversity Framework, a milestone that formalizes its continuous commitment to biodiversity management.
This initiative reflects TNB’s recognition of the need to balance energy infrastructure development with environmental conservation, ensuring that operational growth does not come at the expense of biodiversity ecosystems.
The framework aligns with the targets and actions stipulated in the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) and Malaysia's National Policy on Biological Diversity 2022-2030.
This alignment positions TNB as a player in sustainable development, balancing Malaysia’s energy needs with conservation priorities
Managing Biodiversity Ecosystem
The TNB Biodiversity Framework serves as a guideline for integrating biodiversity conservation into aspects of TNB’s operations.
It ensures that the company addresses the environmental impacts inherent in energy projects while maintaining adherence to international and national sustainability frameworks.
Simply put, this is a systematic approach to managing biodiversity throughout TNB’s project lifecycle—from site planning to decommissioning.
What It Means for TNB
TNB aims to minimize impact on biodiversity caused by its operations and protect the environmental ecosystem.
Environmental Responsibility
To further strengthen TNB’s biodiversity commitment, the company aspires to achieve Net Positive Impact (NPI), particularly for new high biodiversity risk sites.
Operational Integration
Biodiversity conservation is embedded into core business activities, including the development of large-scale solar farms, floating solar, thermal plants, hydroelectric projects, grid networks and other targeted sites, including degraded areas, high biodiversity value areas and locations with eco-tourism potential for other conservation efforts through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
Long-Term Value Creation
Beyond compliance, the framework enables TNB to streamline biodiversity efforts to be more focused and ensure continuity beyond project completion.
This framework signifies TNB’s commitment to a new operational paradigm—one where energy growth and environmental preservation coexist.
It places TNB at the forefront of sustainable infrastructure development in Malaysia and positions the company as a responsible corporate citizen in the global energy landscape.
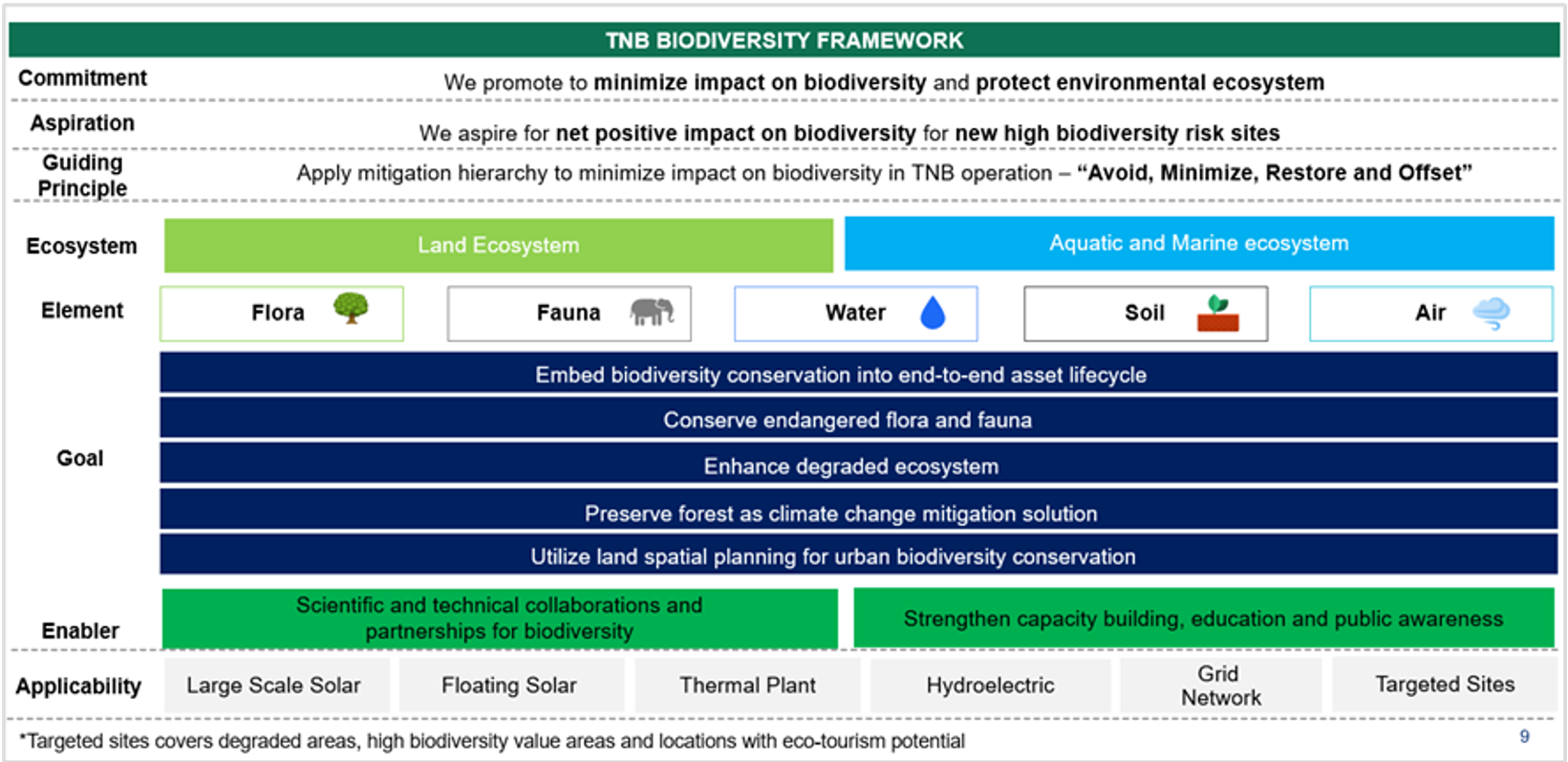
An overview of TNB’s Biodiversity Framework
Understanding Ecosystem Elements and Their Importance
TNB’s biodiversity framework emphasizes that ecosystems are made up of five interconnected elements—flora, fauna, water, soil, and air—which function together to maintain balance.
Disruptions to any one element, such as soil degradation or water contamination, can have cascading effects on the rest of the ecosystem.
The company’s operations interact with aquatic, marine, and land-based ecosystems, making it essential to adopt holistic environmental management practices.
The Mitigation Hierarchy
At the heart of TNB's biodiversity framework is the mitigation hierarchy, a guiding principle to reduce environmental impacts across project lifecycles.
This approach ensures biodiversity considerations are integrated from planning to decommissioning.
The four steps of the mitigation hierarchy are:
Avoid
Refrain activities that could cause irreversible harm to ecosystems. For example, TNB avoids constructing solar farms in protected areas by selecting low-yield agricultural land instead.
Minimize
Take mitigation steps to reduce impacts, such as establishing buffer zones and installation of physical barriers to prevent wildlife conflict.
Restore/Remedy
Rehabilitate ecosystems on-site, such as replanting native vegetation or rescue and translocation of wildlife.
Offset
Compensate for residual impacts through external conservation efforts, including mangrove restoration along coastal regions.
By following this hierarchy, TNB ensures that biodiversity management is effectively implemented across TNB operations.
TNB's Biodiversity Methodology
TNB employs a comprehensive methodology to operationalize its biodiversity framework across various sites.
This methodology is divided into three key phases:
Impact & Risk Assessments
Identify locations with high biodiversity value and quantify biodiversity impact metrics.
Implementing Biodiversity Action Plans (BAPs)
Tailor site-specific strategies to address identified potential impact according to the mitigation hierarchy to support meeting biodiversity goals.
Monitoring & Reporting
Assess and report the changes to the biodiversity ecosystem condition.
This methodology ensures that biodiversity efforts remain data-driven, adaptive with progress measured against defined metrics.
Notably, TNB recognizes and implements various biodiversity initiatives across our operations, contributing to positive impacts on biodiversity conservation and creating value to our environment. Our previous hydro development projects, such as the Ulu Jelai and Hulu Terengganu Hydroelectric Projects, have already demonstrated significant environmental benefits. Building on this success, we continue to enhance and implement best practices through our initiatives such as the Nenggiri Hydroelectric Project, the Bukit Selambau Solar Farm, and the Sultan Azlan Shah Power Station conservation programs.
Nenggiri Hydroelectric Project: Mitigating Environmental Impact
The Nenggiri Hydroelectric Project in Gua Musang, Kelantan, embodies TNB’s commitment to balancing renewable energy production with biodiversity conservation.
The project requires altering river flows and clearing forested land, potentially posing significant risks to land habitat.
To mitigate these impacts, TNB has implemented several biodiversity measures:
Wildlife Monitoring
GPS tracking collars and camera traps are used to monitor animal movements and identify potential conflict zones.
Fish Rescue Operations
Aquatic life is relocated to upstream areas before construction to ensure population survival.
Reforestation Efforts
Nurseries for native plant species have been established to restore forest areas affected by the project.
These efforts demonstrate TNB’s ability to integrate conservation practices into large-scale infrastructure projects, striving for minimal impact to local biodiversity ecosystems.
Bukit Selambau Solar Farm: Renewable Energy in Harmony with Nature
At the Bukit Selambau Solar Farm in Kedah, TNB showcases how innovation can enhance biodiversity within renewable energy projects.
Key biodiversity actions include:
Naturalizing Detention Ponds
Ponds built for stormwater management are repurposed with fish and aquatic plants, forming vibrant ecosystems on-site.
Vegetation Management with Livestocks
TNB collaborates with a local goat farm to use goat grazing for vegetation control, eliminating the need for chemical herbicides.
Behavioral Studies on Macaques
By conducting research on macaque behavior, TNB is developing strategies to manage human-wildlife conflicts effectively.
These initiatives highlight TNB’s commitment to enhancing biodiversity through renewable energy projects, demonstrating that energy and ecology can coexist harmoniously.
Sultan Azlan Shah Power Station: Offsetting Impacts with Long-Term Conservation
The Sultan Azlan Shah Power Station in Manjung, Perak, a coal-fired facility located in a man-made island, showcases TNB’s commitment to offsetting environmental impacts through long-term conservation programs.
Biodiversity initiatives at this site include:
Mangrove Rehabilitation
Since 2013, nearly 20,000 mangrove saplings have been planted along coastal areas to strengthen marine ecosystems and protect shorelines from erosion.
Environmental Monitoring
TNB conducts regular air and water quality assessments within a 5 km radius, ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
Ecological Studies
Every three years, TNB performs ecological assessments to track changes in aquatic and terrestrial flora and fauna.
These efforts demonstrate TNB’s ability to integrate biodiversity offsets into its operations, ensuring long-term sustainability.
A New Era of Sustainable Energy Development
TNB's biodiversity framework represents a significant step forward, embedding environmental stewardship into energy infrastructure development.
By aligning with global and national policies, applying the mitigation hierarchy, and implementing site-specific action plans, TNB aims to adopt the framework in its operations.
This framework is not just a guideline; it is a strategic commitment to sustainable energy growth. TNB is setting a benchmark for sustainable infrastructure development in Malaysia.
The company's efforts ensure that as it powers the nation's future, it also protects its natural heritage for generations to come.